Research from the YouGov-Cambridge Globalism Project last summer revealed most people worldwide agreed the pandemic began in China, but what do Chinese people think?
A team of researchers from the World Health Organisation has begun their hunt for the origins of COVID-19 in China, however research from the YouGov-Cambridge Globalism Project in the Summer showed disagreement within China on where the virus was first detected.
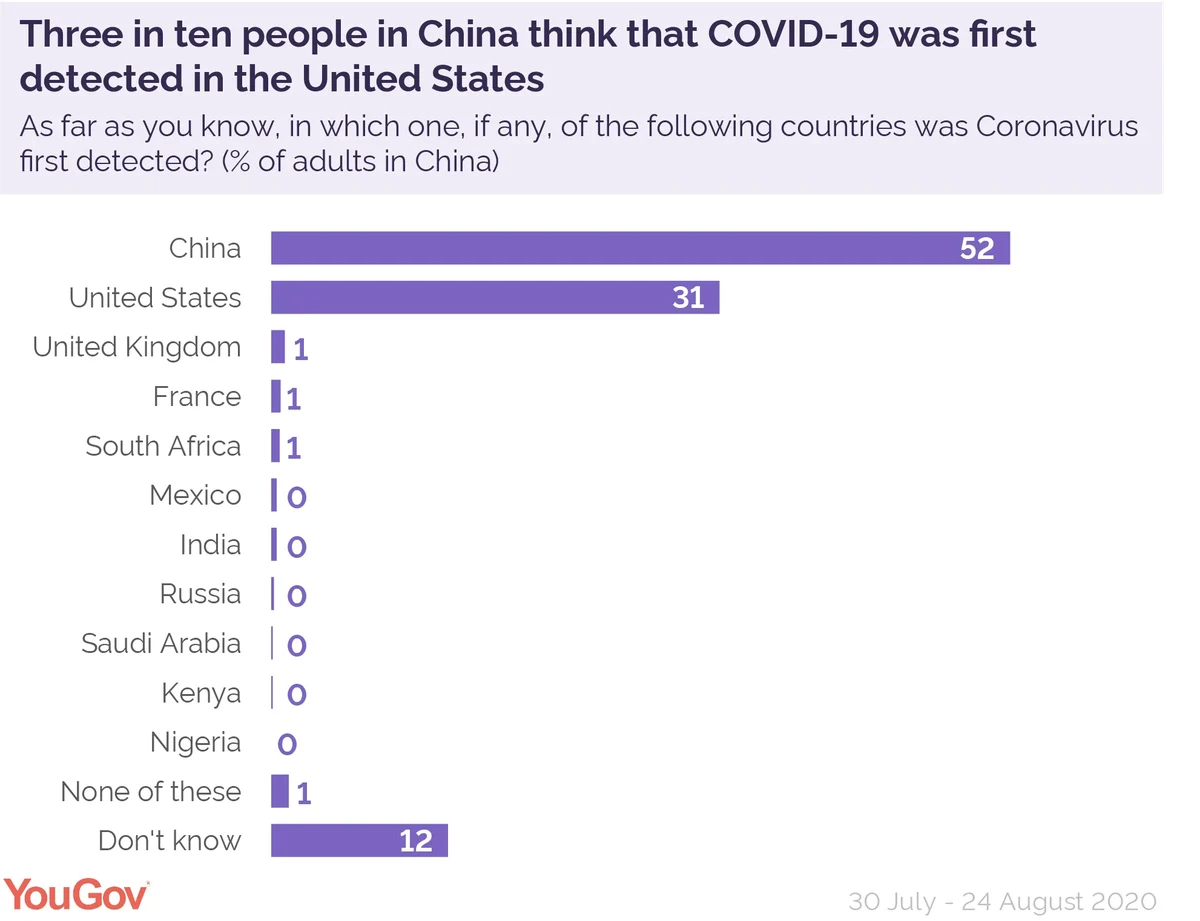
The first cases of COVID-19 were reported in Wuhan, China in December 2019 and around half of people in China (52%) agreed that the virus was first detected within their border. However, three in ten (31%) think that COVID-19 was first detected in the United States, not China.
The second most likely country to think the United States made the first detection of COVID-19 was the United States itself, where 6% of Americans agreed, followed by 5% of Hungarians.
In Summer 2020 less than 1% of Chinese people thought India was the country where COVID-19 was first detected, however Chinese scientists have since claimed that the virus could have originated there.
Elsewhere in the world however, there was a clear consensus, with an average of 92% of people across the other countries surveyed thinking that COVID-19 was first detected in China. The most likely peoples to think this were Nigerians (98%), South Africans (97%), and Greeks (97%).
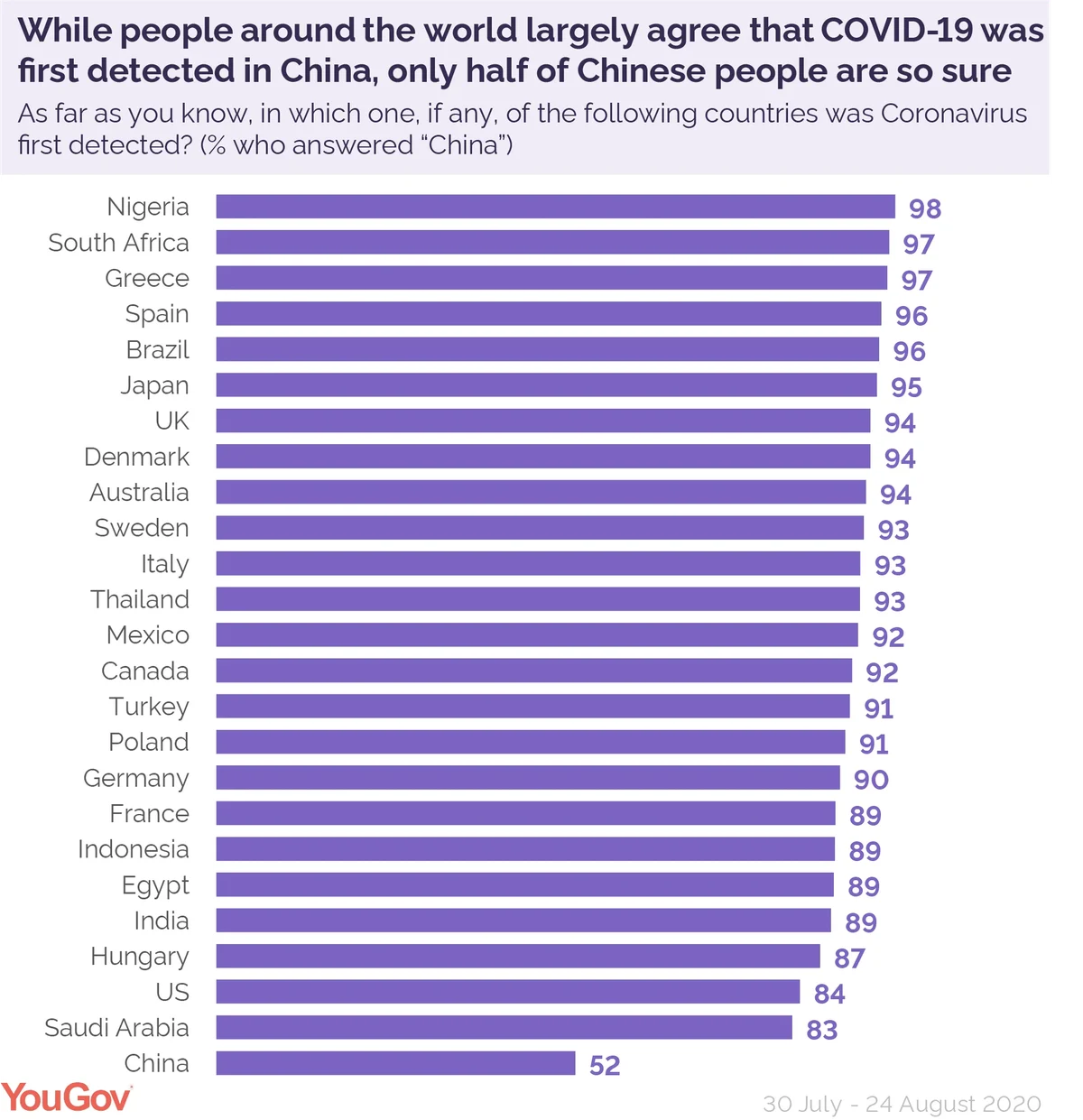
British people were also among the most likely to think the first detection of COVID-19 was in China (94%), as are the same proportion of people in Denmark and Australia.
In France, 89% of people thought the virus was first detected in China, compared to 3% of the French who thought COVID-19 was actually first detected in France.
Despite some of their countrymen believing the United States first detected the virus, 84% of people in the United States instead thought it was China who first detected the virus.
Learn more about the YouGov-Cambridge Globalism Project here
See full results here